CHRONIC DISEASE
Health Disparities: Addressing Chronic Disease Effects in the Latino Community
1. Introduction: What is Chronic Disease?
A chronic disease is a condition that persists for at least one year and requires continuous medical care or restricts everyday activities (link here). The Latino population disproportionately lives below the poverty line, has lower rates of health insurance, and experiences unemployment, which contribute to the growing statistics showing that the Latino community is more likely to experience a greater exposure to chronic diseases (link here).
High-Level Challenges:
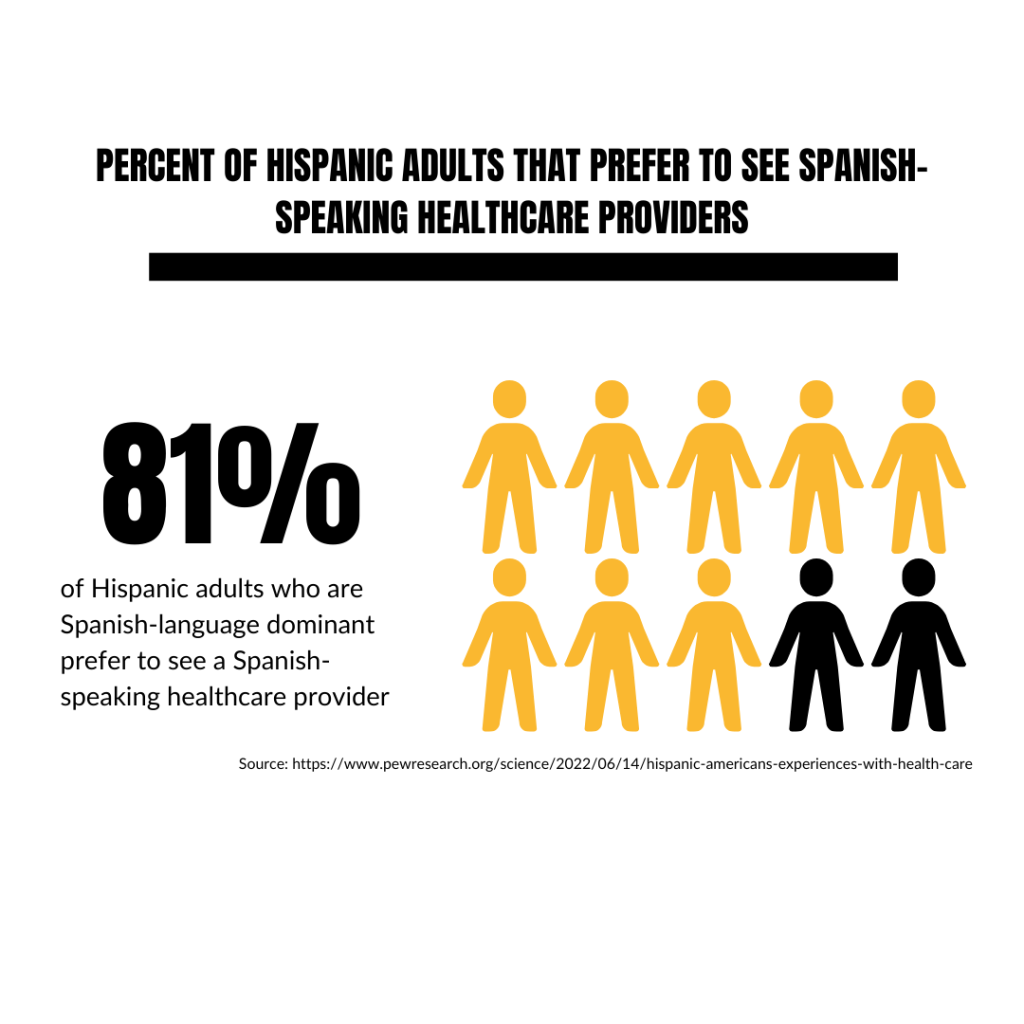
Cultural Representation: Cultural representation in healthcare is critical. Many health resources are unavailable in Spanish or fail to consider cultural factors, such as traditional foods. This lack of culturally and linguistically appropriate information creates gaps in health knowledge and access to care, according to Pew Research Center.
Economic Impact: Hispanic households had a median income of $65,540 in 2023, compared to $89,050 for non-Hispanic white households, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. This income gap contributes to challenges in affording medication, healthcare treatment, and taking unpaid sick days.
Environmental Barriers: Latino communities often face limited access to healthy food and green spaces. Many neighborhoods where Latino families live are classified as food deserts, with few options for nutritious food and limited opportunities for physical activity due to a lack of green spaces, according to PMC.
Health Disparities: Many Latinos face barriers to accessing quality healthcare, including lack of health insurance and language barriers. Limited English proficiency can hinder effective communication with healthcare providers, affecting the quality of care, according to Kansas City University and PMC.
2. Why This Issue Is Important to Latinos
Factors like limited access to healthy food options, lack of safe space for physical activity and socioeconomic disparities can contribute to high rates of these conditions within the Latinx community.
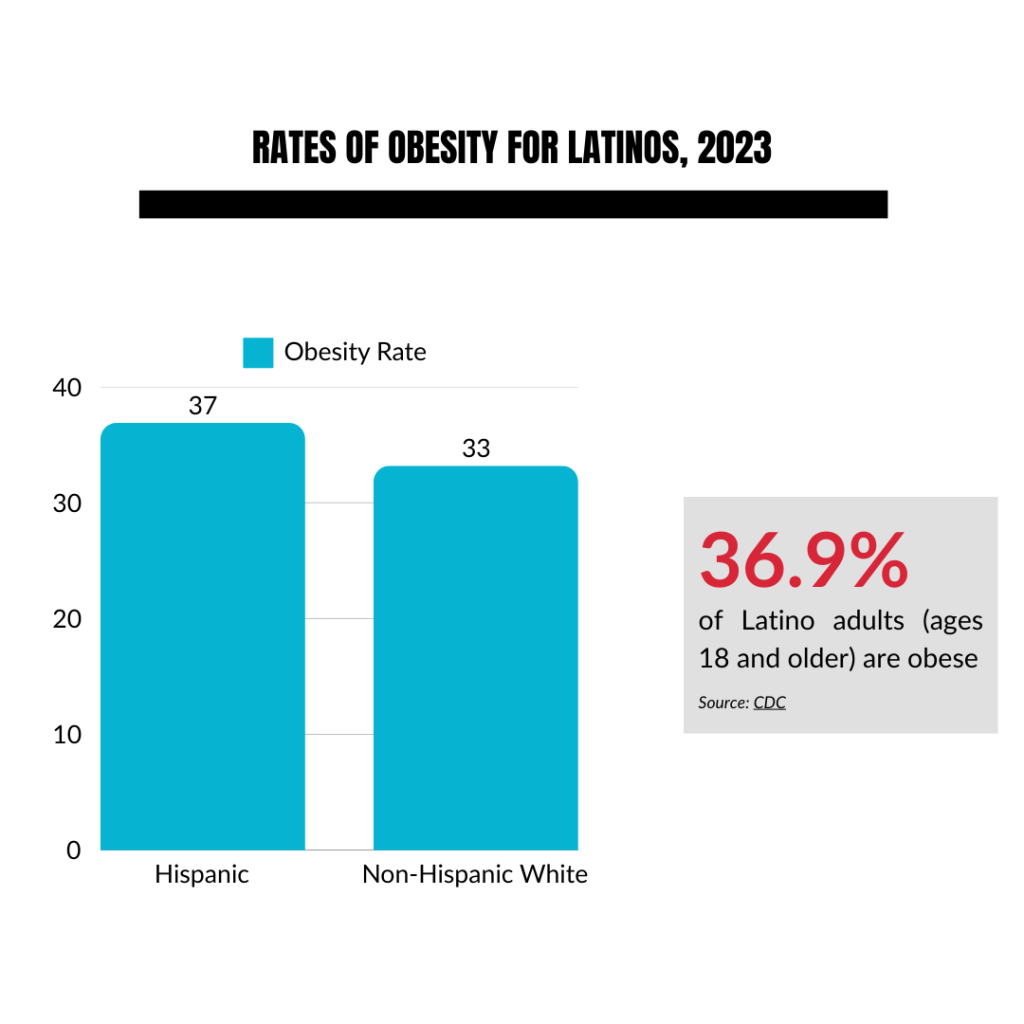
Obesity:
36.9% of Latino adults (ages 18 and older) are obese, compared to 33.2% of non-Hispanic white adults, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Latino communities are more likely to face socio-economic disparities that increase the risk of obesity, including living in food deserts, limited access to healthcare, and health literacy challenges related to language and cultural barriers.
Diabetes:
11.1% of Latino adults are diagnosed with diabetes compared to 8.9% of non-Hispanic white adults, making it one of the leading causes of death, according to the CDC (2023). Higher diabetes rates among Latinos are linked to environmental factors and cultural lifestyle influences.
Cardiovascular Disease:
Cardiovascular disease affects 42.7% of Hispanic women and 52.3% of Hispanic men, making it one of the leading causes of death among Hispanics, according to PMC (2023). Obesity is a common risk factor for both Hispanic men and women, with environmental factors limiting access to affordable, healthy lifestyles.
3. Data: Key Statistics
Health Coverage & Access to Care
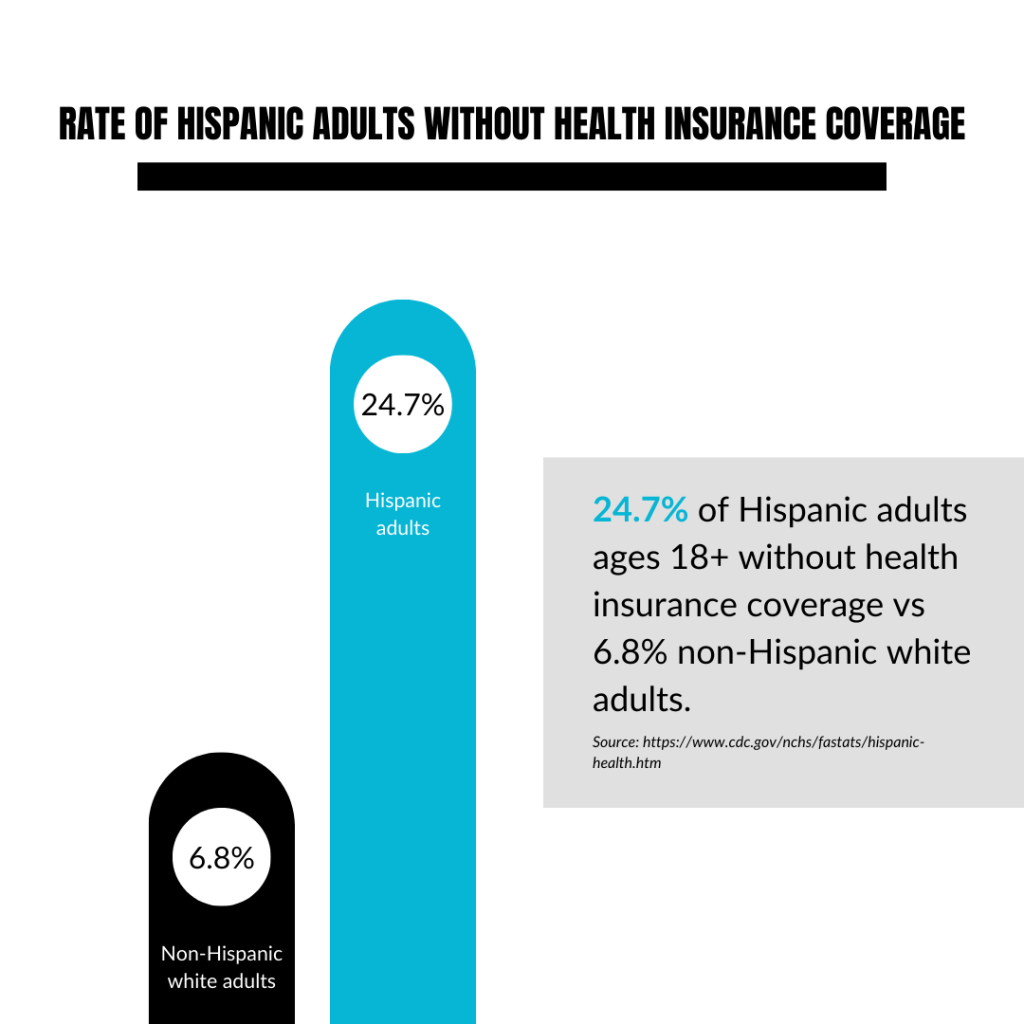
- 24.7% of Latino adults (ages 18 and older) are uninsured, compared to 6.8% of non-Hispanic white adults (Source, 2023).
- 18.9% of Latinos delayed or did not receive needed medical care due to costs, versus 11.8% of non-Hispanic whites (Source, 2023).
- 9.7% of Latinos did not take prescribed medication to save money, compared to 6.9% of non-Hispanic whites (Source, 2023).
- 75% of Latinos visited a doctor for any reason in the past year, compared to 86.2% of non-Hispanic whites (Source, 2023).
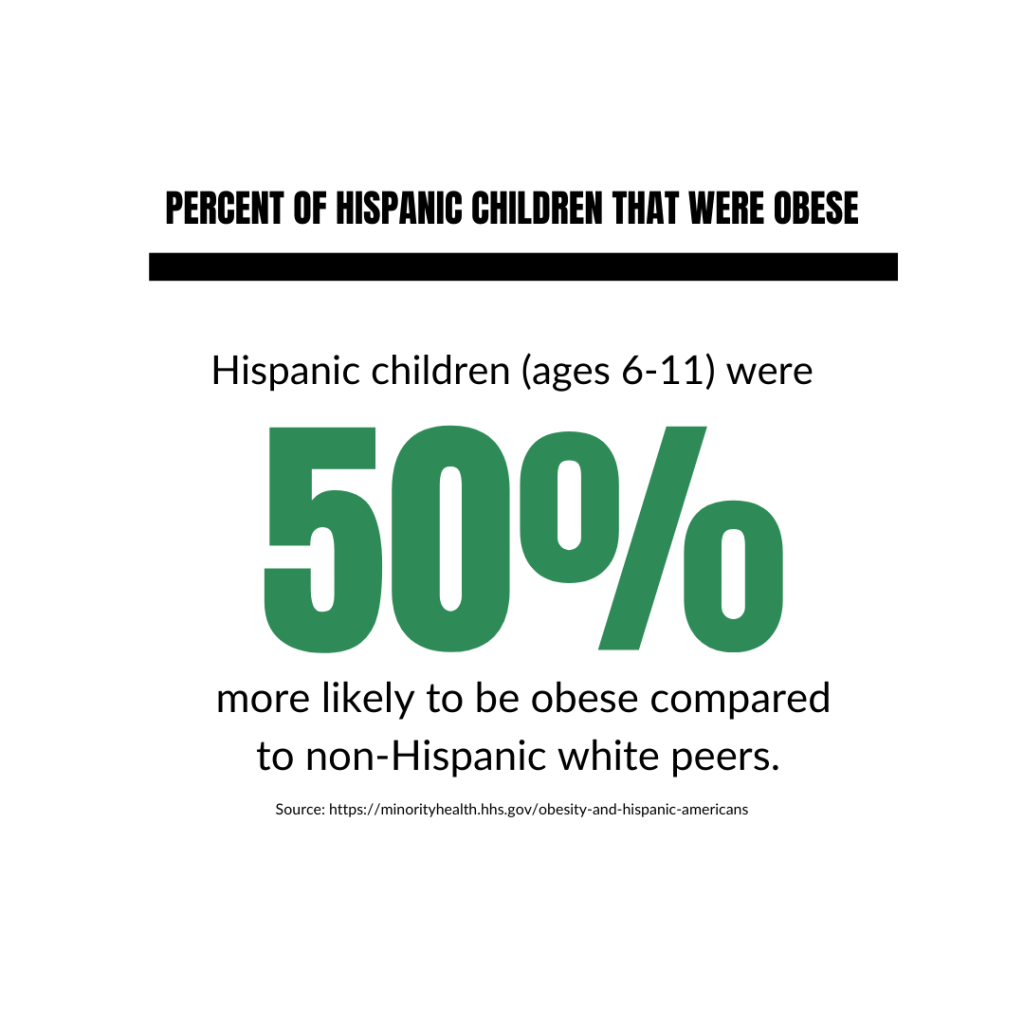
Obesity Rates
- 36.9% of Latino adults (ages 18 and older) are obese, compared to 33.2% of non-Hispanic white adults (Source, 2023).
- From 2015–2018, Hispanic children (ages 6–11) were 1.7 times more likely than non-Hispanic white children to be obese (Source).
- In 2021, Hispanic students (grades 9–12) were 50% more likely to be obese compared to their non-Hispanic white peers (Source).
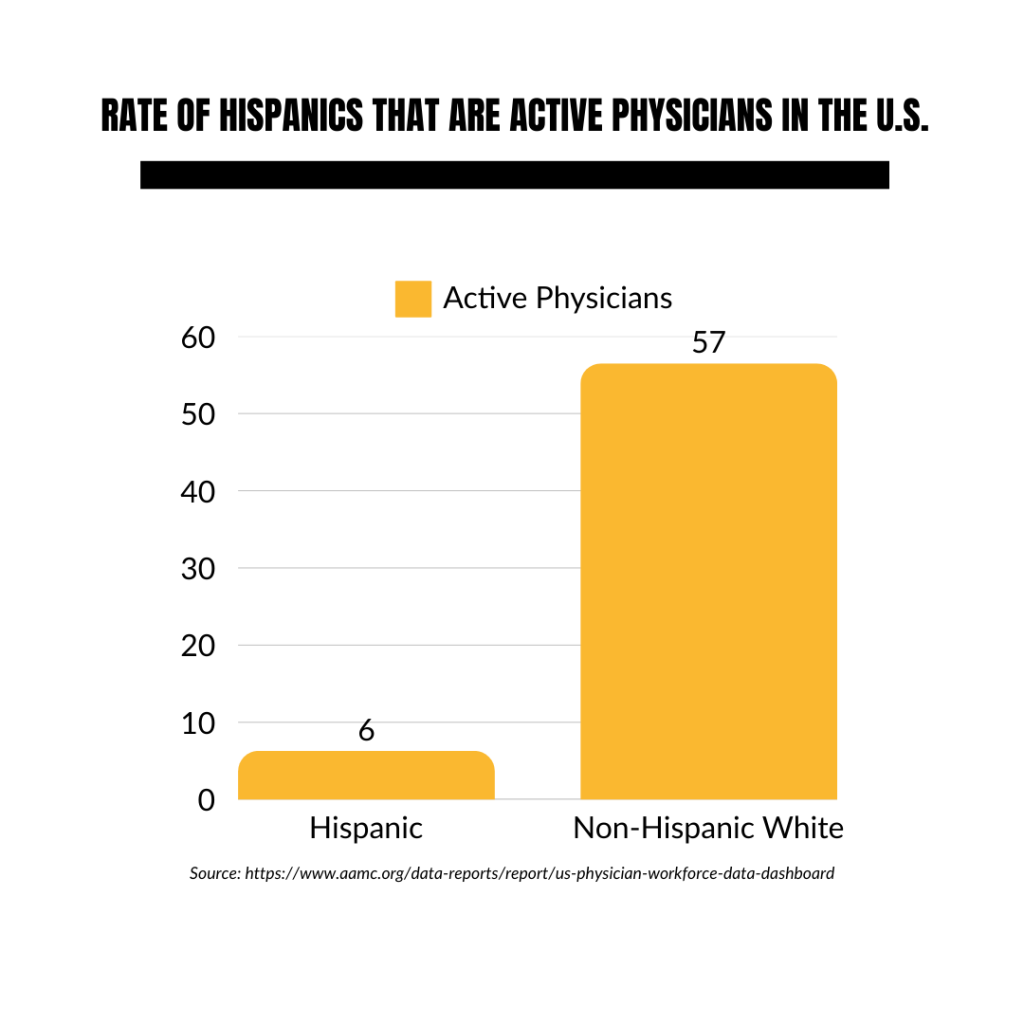
Representation in Healthcare
- 6.3% of active physicians in the U.S. are Hispanic, compared to 56.5% who are non-Hispanic white (Source).
4. Programming, Policies & Recommendations
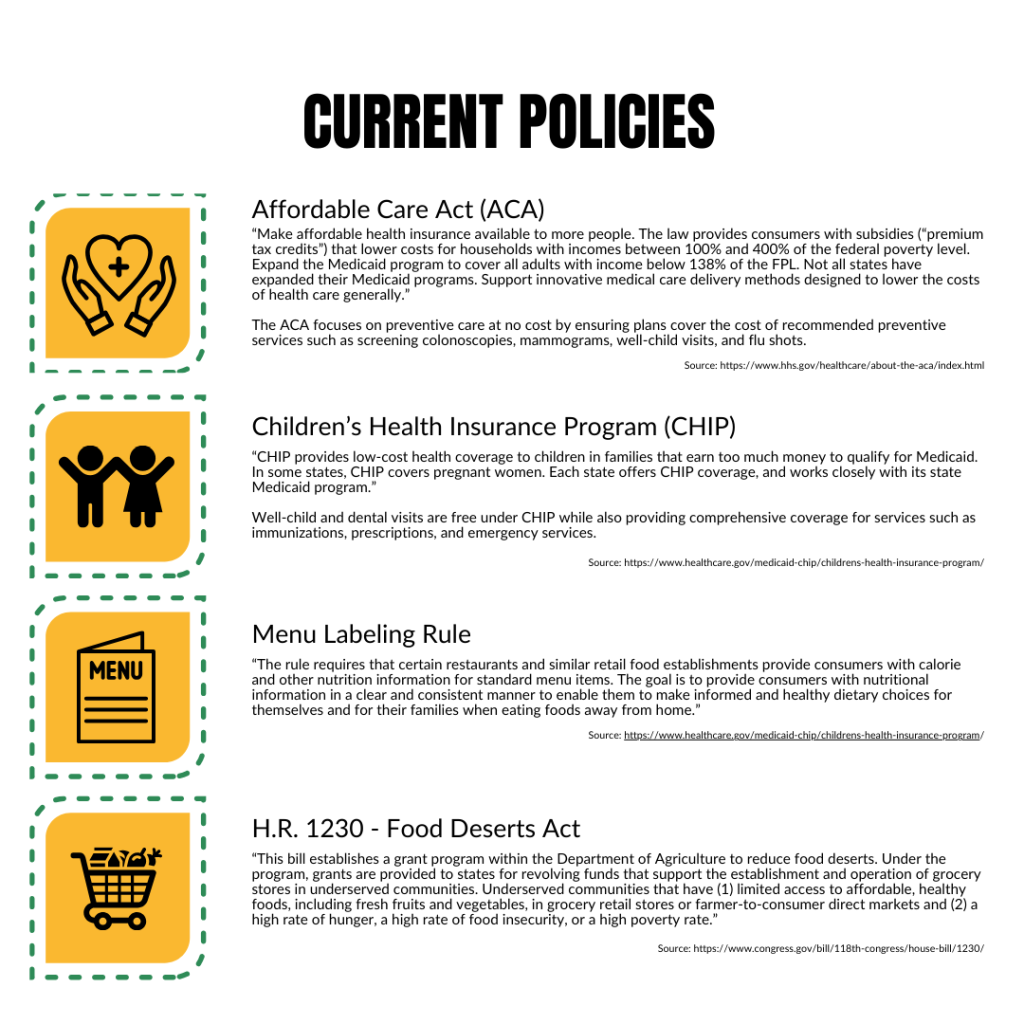
Current Policies
Note: These are existing policies we’ve compiled that are related to Chronic Disease.

Policy and Programmatic Recommendations
Data-driven solutions to further minimize infectious disease spread among U.S. Latinos.
programmatic Recommendations:
1. Community-Based Lifestyle Intervention Programs
- Recommendation: Develop culturally tailored programs focusing on nutrition education, physical activity, and behavioral counseling.
- Supporting Evidence: A study examining the Group Lifestyle Balance program, a community adaptation of the Diabetes Prevention Program, found that participation led to improved health-related quality of life among adults with pre-diabetes and metabolic syndrome. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
2. Expand Access to Preventive Health Screenings
- Recommendation: Organize free or low-cost screening events for blood pressure, cholesterol, BMI, and blood glucose in community hubs like churches, schools, and community centers.
- Supporting Evidence: While specific studies on community-based screenings are limited, the general consensus in public health emphasizes the importance of early detection through accessible screenings to prevent disease progression, especially in underserved communities. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov and https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/preventive-care
- Additionally, integrating community health workers (CHWs) into screening programs has proven beneficial. A publication from The Community Guide outlines the effectiveness of engaging CHWs to increase cancer screening rates, highlighting their role in improving health outcomes through community-based interventions. thecommunityguide.org
3. Train and Deploy Community Health Workers (Promotores de Salud)
- Recommendation: Utilize bilingual, culturally competent community health workers to provide education, chronic disease management support, and navigation of healthcare systems.
- Supporting Evidence: Research indicates that interventions by community-based health workers are effective in improving health outcomes and are cost-effective for certain health conditions, particularly when partnering with low-income, underserved, and racial and ethnic minority communities. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
4. Nutrition and Physical Activity Policy Advocacy
- Recommendation: Advocate for policies that increase access to healthy foods (e.g., farmers’ markets, school nutrition programs) and create safe, accessible spaces for physical activity in Latino neighborhoods.
- Supporting Evidence: The “Food Is Medicine” movement highlights the critical role of access to healthy food in preventing and managing diet-related chronic diseases. Programs providing “produce prescriptions” have shown positive health outcomes, emphasizing the need for systemic change to improve public health through better nutrition. time.com
5. Culturally Relevant Diabetes Self-Management Education (DSME) Programs
- Recommendation: Implement DSME programs that are bilingual and integrate cultural practices, focusing on goal-setting, healthy eating, medication adherence, and stress management.
- Supporting Evidence: A culturally adapted behavioral intervention for Latino adults at high risk of diabetes demonstrated effectiveness in weight loss, underscoring the importance of culturally tailored programs in chronic disease prevention. jamanetwork.com

Policy Recommendations:
Informed by Evidence: Policy Recommendations from Experts
Enhance Access to Affordable Healthcare
- Policy Action: Expand healthcare coverage and reduce financial barriers to ensure Latino individuals can access preventive services and manage chronic conditions effectively.
- Rationale: Latinos are less likely to receive evidence-based care and more likely to have chronic diseases.
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Implement Culturally Tailored Health Promotion Campaigns
- Policy Action: Develop and disseminate health education materials in Spanish and other relevant languages, incorporating cultural values and practices to enhance engagement.
- Rationale: Culturally relevant programs have been shown to improve health outcomes among Latino populations.
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Support Community Health Worker (Promotores de Salud) Programs
- Policy Action: Fund and integrate community health workers into healthcare teams to provide culturally competent education, outreach, and support services.
- Rationale: Promotores serve as liaisons between their community and health professionals, effectively addressing health disparities.A study published in the American Journal of Public Health found that CHW interventions led to better diabetes management among Latino and African American adults.
Promote Access to Healthy Foods and Physical Activity
- Policy Action: Advocate for policies that increase the availability of nutritious foods and create safe spaces for physical activity in Latino neighborhoods.
- Rationale: Addressing environmental factors can significantly reduce chronic disease risk in Latino communities. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Enhance Data Collection on Latino Health Disparities
- Policy Action: Mandate the collection and analysis of health data disaggregated by ethnicity to inform targeted interventions and policy decisions.
- Rationale: Disaggregated data provides a more accurate picture of health disparities among different racial and ethnic subgroups. An article in the American Journal of Public Health emphasizes that detailed racial/ethnic data is crucial for advancing health equity and reducing disparities. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

5. Call to Action: Get Involved
Chronic diseases are a growing crisis in the Latinx community, driven by health disparities and economic barriers like limited insurance coverage and high out-of-pocket costs. This leads to missed workdays, financial strain, and reduced quality of life. Addressing these issues through community involvement and advocacy can break down barriers, improve access to care, and reduce chronic disease disparities—moving us closer to health equity.
Take Action for Health Equity!
Ready to make a difference? Here are fun and impactful ways to get involved:
📣 1. Use Your Voice—Advocate for Change!
- Contact Your Legislators: Speak up for policies that promote health equity—locally, statewide, and nationwide!
- Join Advocacy Programs:
🤝 2. Volunteer Your Time
- Support organizations fighting for health equity in Latino communities.
- Lend your skills to local health initiatives or community events.
🍎 3. Learn & Live Healthier—Locally!
- Find Local Programs: Look for culturally relevant programs that focus on:
- Nutrition Education: Cooking classes with healthy twists on traditional Latino foods.
- Physical Activity: Fun classes like Zumba to get moving and stay active!
💡 Every action counts—your voice, time, and energy can help build healthier communities!
6. Partners and Resources for Families
🤝 Our Core Partners
Tu Salud ¡Sí Cuenta!
Promoting healthier lifestyles in Latino communities.
At LUCHAR, our partnership with Tu Salud ¡Sí Cuenta! amplifies efforts to promote healthy habits through culturally relevant programs focused on nutrition, physical activity, and chronic disease prevention. Together, we empower Latino families to make informed health decisions that improve long-term well-being.
Learn more about Tu Salud ¡Sí Cuenta!
Healthier Texas
Creating a healthier future for all Texans.
Through our collaboration with Healthier Texas, LUCHAR supports initiatives that address chronic disease prevention across the state. Together, we promote community-driven health programs, focusing on equity, access to care, and sustainable lifestyle changes to reduce health disparities in Latino communities.
Learn more about Healthier Texas
Unidos Contra la Diabetes
Empowering communities to prevent and manage diabetes through education and advocacy.
LUCHAR partners with Unidos Contra la Diabetes to address the growing impact of diabetes in the Rio Grande Valley. Together, we promote health equity through culturally tailored programs focused on diabetes prevention, early detection, and community-driven support.
Learn more about Unidos Contra la Diabetes
National Alliance for Hispanic Health – Healthy Americas Foundation
Improving the health and well-being of Latino communities nationwide.
Our collaboration with the Healthy Americas Foundation strengthens LUCHAR’s mission to address chronic disease disparities. Together, we promote health literacy, advocate for equitable health policies, and support programs that improve access to quality care for Latino communities across the U.S.
Learn more about Healthy Americas Foundation
Additional Resources for Families
- Latinas Contra Cancer
Website: https://www.latinascontracancer.org/programs
Description: Supports prevention, detection, treatment, and survivorship by eliminating barriers to high-quality healthcare facing the Latiné community. - American Diabetes Association
Website: https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes
Description: Focuses on tackling critical challenges in diabetes care and prevention, improving diabetes management, addressing obesity, and advancing health equity. - MyPlate for Kids
Website: https://www.myplate.gov/life-stages/kids
Description: Provides recipes and resources to support healthy, budget-friendly meals, with family-friendly activities, games, and resources available in Spanish. - National Alliance for Hispanic Health – Buena Salud Club
Website: https://www.healthyamericas.org/current-programs
Description: Offers free membership to promote healthy lifestyles and provide health information in English and Spanish. - Hispanic Health Coalition – ¡Vive tu Vida! Get Up! Get Moving!
Website: https://hispanic-health.org/
Description: Hosts events promoting healthy eating and active living for families of all ages. - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Healthy Living Resources
Website: https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/healthy_eating/index.html
Description: Offers guidelines and tips for healthy eating, physical activity, and weight management, with Spanish-language resources. - American Heart Association – Healthy for Good
Website: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living
Description: Provides resources on healthy eating, physical activity, and well-being, including recipes and wellness tips. - Tu Salud ¡Sí Cuenta!
Website: https://sph.uth.edu/research/centers/hispanic-health/tu-salud-si-cuenta/
Description: Offers free programs like yoga and diabetes management classes tailored for Latino communities. - Latino Health Access (LHA)
Website: https://www.latinohealthaccess.org/
Description: Provides programs focusing on disease prevention, chronic disease management, and health education. - National Kidney Foundation
Website: https://www.kidney.org/news-stories/kidney-disease-hispanic-latino-communities-causes-and-prevention
Description: Offers resources about kidney disease prevention and management, with materials available in Spanish.
Additional Resources for Partners
- Hispanic Health Coalition
Website: https://hispanic-health.org/
Description: Focuses on advancing health equity through education, advocacy, and research. - National Alliance for Hispanic Health
Website: https://www.healthyamericas.org/current-programs
Description: Provides programs and resources to improve health outcomes in Latino communities nationwide. - American Diabetes Association – Advocacy
Website: https://diabetes.org/advocacy
Description: Offers advocacy tools and resources to influence public policy related to diabetes care and prevention. - Center for Chronic Care Innovation – HealthPartners Institute
Website: https://www.healthpartners.com/institute/centers/center-for-chronic-care-innovation/
Description: Connects research with practice to improve population health outcomes through innovative strategies. - National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion – CDC
Website: https://www.cdc.gov/health-equity-chronic-disease/index.html
Description: Provides data, tools, and strategies to advance health equity and prevent chronic diseases. - National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS)
Website: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/
Description: Offers comprehensive health statistics to support research and policy-making. - Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP)
Website: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/
Description: Provides healthcare data to support analysis of healthcare utilization, costs, and chronic disease trends.
7. References
- American Diabetes Association. (2024). About Diabetes. Retrieved from https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes
- American Diabetes Association. (2024). Advocacy. Retrieved from https://diabetes.org/advocacy
- Association of American Medical Colleges. (2024). U.S. Physician Workforce Data Dashboard. Retrieved from https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/report/us-physician-workforce-data-dashboard
- California Secretary of State. (2024). Voter Guide. Retrieved from https://voterguide.sos.ca.gov/propositions/
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). About Chronic Diseases. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/chronic-disease/about/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, October 20). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/
- Healthy Americas Foundation. (2024). Current Programs. Retrieved from https://www.healthyamericas.org/current-programs
- Hispanic Health Coalition. (2024). Home. Retrieved from https://hispanic-health.org/
- Latinas Contra Cancer. (2024). Programs. Retrieved from https://www.latinascontracancer.org/programs
- National Institutes of Health. (2024). The Role of Health Literacy in Chronic Disease Management. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5044865/
- U.S. Census Bureau. (2024). Income and Poverty in the United States: 2023. Retrieved from https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/2024/demo/p60-282.pdf
- U.S. Congress. (2024). H.R.6331 – Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act of 2008. Retrieved from https://www.congress.gov/bill/110th-congress/house-bill/6331
- Vote411.org. (2024). Home. Retrieved from https://www.vote411.org/
- PMC. (2024). Cardiovascular Disease in Hispanic Populations. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9161759/
- Pew Research Center. (2024). Hispanic Americans’ Experiences with Health Care. Retrieved from https://www.pewresearch.org/
- The Community Guide. (2024). Effectiveness of Community Health Workers in Chronic Disease Prevention. Retrieved from https://www.thecommunityguide.org/
- Time. (2024). The Role of Food in Chronic Disease Prevention. Retrieved from https://time.com/7005880/americans-prescriptions-healthy-food-is-medicine/
- JAMA Network. (2024). Culturally Adapted Interventions for Latino Diabetes Prevention. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/
